之前写的两个项目中,有使用过java调用dll,之前一直使用jni进行调用。最近在了解jdk21时,其中有个更新让我感兴趣,JEP 442[Foreign Function & Memory API (Third Preview)],是对外部函数和堆外内存访问的API更新。并且在检索发现,jdk17孵化的版本和jdk21的三次预览的版本的api还是不太一样的。
Memory segments 和 arenas
Memory segments(内存段)是由位于堆外或堆上的连续内存区域在java中的抽象。
可以使用Arena来申请内存段,每个段都提供存储空间,并且为了安全这个空间的使用有时间界限的。
Arena在申请内存时,可以定义该内存的使用期限。创建一个100bytes的native连续内存段。其中Arena定义的是内存段的生命周期。
-
global提供了无限的生命周期。这段内存的申请永远不会被释放掉。
MemorySegment data = Arena.global().allocate(100); -
ofAuto,直到jvm的垃圾收集器检测到该内存段不可访问。该内存就会被释放。
void processData() { MemorySegment data = Arena.ofAuto().allocateNative(100); } 方法结束后,data被释放 -
try-with-resource方式释放内存
MemorySegment input = null, output = null; try (Arena processing = Arena.ofConfined()) { input = processing.allocate(100); ... set up data in 'input' ... output = processing.allocate(100); ... process data from 'input' to 'output' ... ... calculate the ultimate result from 'output' and store it elsewhere ... } // 内存段在这里被释放
Dereferencing内存段
Dereferencing内存段(不知道这个翻译成什么)。大概理解成,在对引用字段申请内存时:
- 需要知道申请的内存总大小。
- 要使每个值的字段地址对齐。
- 要明确存储的java类型和顺序
对官方用例做了一些修改来明确他的说法。
用例中将长度为25的int数组写入内存中,申请内存时使用java_int的内存对齐大小*申请数量。
MemorySegment会在调用setAtIndex时自动对齐。
public static void dereferenceSegments() throws Throwable {
long byteAlignment = JAVA_INT.byteAlignment();
int arraySize = 25;
MemorySegment segment
= Arena.ofAuto().allocate(byteAlignment * arraySize, byteAlignment);
//写入
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) {
segment.setAtIndex(ValueLayout.JAVA_INT, i, i);
//等价于 segment.setAtIndex(ValueLayout.JAVA_INT, i * byteAlignment, i);
}
//读出
for (int i = 0; i < arraySize; i++) {
int i1 = segment.get(JAVA_INT, i * byteAlignment);
System.out.println(i1);
int i2 = segment.getAtIndex(JAVA_INT, i);
System.out.println(i2);
}
}
Memory layouts与结构体
使用Memory layouts(内存布局)来定义结构体
struct Point {
int x;
int y;
} pts[10];
如果使用dereference的方式去写入该结构体,虽然已经对齐结构体,但在设值时还要进行字段对齐。
MemorySegment segment
= Arena.ofAuto().allocate(2 * ValueLayout.JAVA_INT.byteSize() * 10, // size
ValueLayout.JAVA_INT.byteAlignment); // alignment
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
segment.setAtIndex(ValueLayout.JAVA_INT,
/* index */ (i * 2),
/* value to write */ i); // x
segment.setAtIndex(ValueLayout.JAVA_INT,
/* index */ (i * 2) + 1,
/* value to write */ i); // y
}
可以使用MemoryLayout创建内存布局。
定义结构体内存布局structLayout,利用sequenceLayout创建10个重复的struct相当的内存,并对齐结构体和字段。
创建变量内存访问句柄去访问字段值,根据布局路径,先使用sequence index筛选结构体,再使用group name筛选字段。
StructLayout structLayout = MemoryLayout.structLayout(
JAVA_INT.withName("x"),
JAVA_INT.withName("y"));
SequenceLayout ptsLayout = MemoryLayout.sequenceLayout(10, structLayout);
VarHandle xHandle
= ptsLayout.varHandle(PathElement.sequenceElement(),
PathElement.groupElement("x"));
VarHandle yHandle
= ptsLayout.varHandle(PathElement.sequenceElement(),
PathElement.groupElement("y"));
MemorySegment segment = Arena.ofAuto().allocate(ptsLayout);
for (int i = 0; i < ptsLayout.elementCount(); i++) {
xHandle.set(segment,
/* index */ (long) i,
/* value to write */ i); // x
yHandle.set(segment,
/* index */ (long) i,
/* value to write */ i); // y
}
内存段分配器
内存段也能从Segment allocators中获得。与直接使用Arena分配不同的是,Segment allocators可以提前分配比较大的内存段,在向他申请内存时,他会返回提前分配的一部分内存来响应分配请求。以下代码,涉及的native内存的分配只有一次(应该是为了提高allocate效率)
MemorySegment segment = Arena.ofAuto().allocate(100);
SegmentAllocator allocator = SegmentAllocator.slicingAllocator(segment);
for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) {
MemorySegment s = allocator.allocateArray(JAVA_INT,
1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
}
查找外部函数
SymbolLookup::libraryLookup(String, Arena):加载指定lib的symbols,作用在指定arena内
SymbolLookup::loaderLookup():查找指定 System::loadLibrary and System::load相同的symbol
Linker::defaultLookup():查找系统自带的c/c++标准库
Linker linker = Linker.nativeLinker();
SymbolLookup defaultLookup = linker.defaultLookup();
SymbolLookup symbolLookup = SymbolLookup.libraryLookup("src\\main\\resources\\MathLibrary.dll", Arena.global());
链接到外部函数
interface Linker {
MethodHandle downcallHandle(MemorySegment address,
FunctionDescriptor function);
MemorySegment upcallStub(MethodHandle target,
FunctionDescriptor function,
Arena arena);
}
对于向下调用,该downcallHandle方法获取外部函数的地址(通常是MemorySegment从库查找中获得的地址)并将外部函数公开为向下调用方法句柄MethodHandle,通过调用句柄invoke执行。
对于向上调用,该upcallStub方法采用一个方法句柄(通常是指 Java 方法,而不是向下调用方法句柄)并将其转换为实例MemorySegment。随后,当 Java 代码调用向下调用方法句柄时,内存段将作为参数传递。实际上,内存段充当函数指针。
向下调用
在调用外部函数前,了解一下函数描述对象的构造方法,第一个为返回值内存布局,剩余为传入参数内存布局。
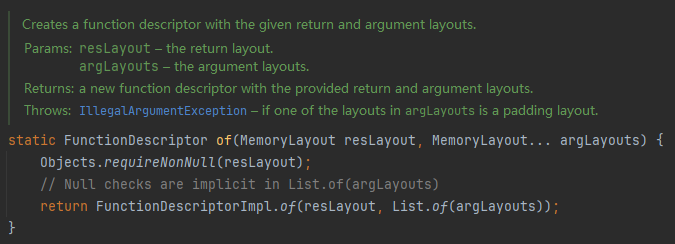
假设我们希望从 Java 向下strlen调用标准 C 库中定义的函数:
size_t strlen(const char *s);
Linker linker = Linker.nativeLinker();
SymbolLookup defaultLookup = linker.defaultLookup();
MethodHandle strlenHandle = linker.downcallHandle(
defaultLookup.find("strlen").orElseThrow(),
FunctionDescriptor.of(JAVA_LONG, ADDRESS)
);
try (Arena offHeap = Arena.ofConfined()) {
MemorySegment pointers = offHeap.allocateUtf8String("Hello world!");
System.out.println(strlenHandle.invoke(pointers)); //11
}
更复杂的尝试,我们希望定义一个结构体Point,并且传入Point数组,链接到C函数找到x和y相加最大的Point,定义以下DLL
// MathLibrary.h - Contains declarations of math functions
#pragma once
#ifdef MATHLIBRARY_EXPORTS
#define MATHLIBRARY_API __declspec(dllexport)
#else
#define MATHLIBRARY_API __declspec(dllimport)
#endif
struct Point {
int x;
int y;
};
extern "C" MATHLIBRARY_API Point test_point(Point points[], long count);
// MathLibrary.cpp : Defines the exported functions for the DLL.
#include "pch.h"
#include <utility>
#include <limits.h>
#include "MathLibrary.h"
#include <iostream>
// cpp文件内容
Point test_point(Point points[],long count)
{
if (count <= 0) {
// Return a default Point with x and y set to 0
Point defaultPoint = { 0, 0 };
return defaultPoint;
}
Point maxPoint = points[0];
int maxSum = maxPoint.x + maxPoint.y;
for (int i = 1; i < count; ++i) {
int currentSum = points[i].x + points[i].y;
if (currentSum > maxSum) {
maxSum = currentSum;
maxPoint = points[i];
}
}
int x = maxPoint.x;
int y = maxPoint.y;
std::cout << "x = " << x << ", y = " << y << std::endl;
return maxPoint;
}
用前面了解到的方法,利用内存布局创建基于结构体的序列布局,基于函数名和函数描述对象现在函数句柄,创建变量内存访问句柄去设置字段值。
public static void dereferenceSegmentsStruct() throws Throwable {
StructLayout structLayout = MemoryLayout.structLayout(
JAVA_INT.withName("x"),
JAVA_INT.withName("y"));
MethodHandle test_point = linker.downcallHandle(
symbolLookup.find("test_point").orElseThrow(),
FunctionDescriptor.of(structLayout, ADDRESS, JAVA_LONG)
);
SequenceLayout ptsLayout = MemoryLayout.sequenceLayout(10, structLayout);
VarHandle xHandle
= ptsLayout.varHandle(PathElement.sequenceElement(),
PathElement.groupElement("x"));
VarHandle yHandle
= ptsLayout.varHandle(PathElement.sequenceElement(),
PathElement.groupElement("y"));
MemorySegment segment = Arena.ofAuto().allocate(ptsLayout);
for (int i = 0; i < ptsLayout.elementCount(); i++) {
xHandle.set(segment, (long) i, i);
yHandle.set(segment, (long) i, i);
}
SegmentAllocator allocator = SegmentAllocator.slicingAllocator(Arena.ofAuto().allocate(structLayout.byteSize()));
MemorySegment result = (MemorySegment) test_point.invoke(allocator, segment, ptsLayout.elementCount());
result = result.reinterpret(structLayout.byteSize());
VarHandle resultX
= structLayout.varHandle(PathElement.groupElement("x"));
VarHandle resultY
= structLayout.varHandle(PathElement.groupElement("y"));
System.out.println(StringTemplate.STR. "\{ resultX.get(result) }:\{ resultY.get(result) }" );
}
在创建MethodHandle时,注意描述符的正确性,其特殊性在于:
传入Point数组时,需要使用地址布局传入(对象内存已初始化赋值完毕)
返回Point对象时,需要使用结构体布局作为返回,并且需要使用内存段分配器为结构体分配内存(对象内存未初始化)。
向上调用
使java代码作为函数指针传递到某个外部函数中调用。
考虑到标准c库中有函数qsort。用于对数组进行快速排序。这个函数接受以下参数:
void* base:指向待排序数组的指针,数组的每个元素的大小为size字节。size_t nmemb:数组中元素的数量。size_t size:每个元素的大小(以字节为单位)。int (*compar)(const void*, const void*):一个函数指针,用于比较数组中的两个
void qsort(void *base, size_t nmemb, size_t size,
int (*compar)(const void *, const void *));
所使用的函数指针可以用java定义一个Qsort类
public class Qsort {
static int qsortCompare(MemorySegment elem1, MemorySegment elem2) {
return Integer.compare(elem1.get(JAVA_INT, 0), elem2.get(JAVA_INT, 0));
}
}
现在,我们可以使用Linker根据方法句柄获取到方法的内存段,将他和其他参数一同传递给已链接的外部函数。如下:
public static void lookingUpForeignFunctions() throws Throwable {
MethodHandle qsort = linker.downcallHandle(
defaultLookup.find("qsort").orElseThrow(),
FunctionDescriptor.ofVoid(ADDRESS, JAVA_LONG, JAVA_LONG, ADDRESS)
);
MethodHandle comparHandle
= MethodHandles.lookup()
.findStatic(Qsort.class, "qsortCompare",
MethodType.methodType(int.class,
MemorySegment.class,
MemorySegment.class));
MemorySegment comparFunc
= linker.upcallStub(comparHandle,
/* A Java description of a C function
implemented by a Java method! */
FunctionDescriptor.of(JAVA_INT,
ADDRESS.withTargetLayout(JAVA_INT),
ADDRESS.withTargetLayout(JAVA_INT)),
Arena.ofAuto());
try (Arena arena = Arena.ofConfined()) {
MemorySegment array
= arena.allocateArray(ValueLayout.JAVA_INT,
0, 9, 3, 4, 6, 5, 1, 8, 2, 7);
qsort.invoke(array, 10L, ValueLayout.JAVA_INT.byteSize(), comparFunc);
int[] sorted = array.toArray(JAVA_INT); // [ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 ]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sorted));
}
}
零长度内存段
外部函数通常分配一个内存区域并返回指向该区域的指针。FFM API 将从外部函数返回的指针表示为零长度内存段。段的地址是指针的值,段的大小为零。类似地,当从内存段读取指针时,则返回零长度内存段。
零长度段不具有空间,因此访问此类段都会失败并抛出IndexOutOfBoundsException。我们可以通过MemorySegment::reinterpret将零长度内存段转换成其内存段的真实大小,就像我们在向下调用结构体中代码片段result = result.reinterpret(structLayout.byteSize());一样。但这可能会尝试引用该区域边界之外的内存,这可能会导致 JVM 崩溃或无提示内存损坏。
